What is the result of the evolution of the plant world? Raising plant organization
A variety of all previously living plants on our planet is the result of evolutionary processes. The classification of all existing species gives almost a complete picture of how the evolution of the plant world occurred in various systematic groups.
All floral world can be divided into two main groups - lower and higher plants. Lower plants are lichen, algae, cyanobacteria, actinomycetes and pylofitis.
Top species include: various mosses, a variety of ferns, chests and planes, coated and viced plants. The same group includes extinct and no longer existing plisforms.
Proof of what the evolution of the plant world occurred is numerous finds of paleontologists. Fossil remains of ancient plants are found everywhere, among them, stromatolys can be distinguished - these are formation of residual algae, which dwells in the oceans and seas. Prints of huge ferns, plane and horsages still detect in the deposits of peatlands or coal.
The evolution of the plant world took place in several stages. The first stage can be called the appearance of the very first microorganisms - single-cell algae of cyanobacteria, it happened in the Archean Era.
The next stage is the appearance of eukaryotov, their emergence occurred more than one and a half billion years ago. Eukarotes were ancestors of unicellular algae, which in turn became the progenitors of multicellular algae.
The next important stage is the appearance of some plants on land. It is believed that the very first were psofithi. Now they already belong to the extinct group, but they were precisely the transitional form from the lower forms to the higher.
Psulfiti had a coating tissue with stories that protected the plant from the effects of the external environment, and the mechanical tissue that performed the reference functions.
The evolution of the plant world continued, and the next stage one can characterize the complete domination of ferns. This stage falls on the coal period. Ferns had a well-developed conductive and root system and leaves as the necessary organ for photosynthesis.
Thus, ferns were fully adapted for life on land. The reproduction of these plants was closely related to the presence of water, their appearance significantly enriched the atmosphere with oxygen.
Already later, seed ferns appeared, which are now no longer in nature. They were the ancestors of today's gone plants. The presence of seed made the reproduction of ferns independent from the presence of water.
In the Perm period, the wet climate was reduced dry, precisely at this time and gamotional plants appeared. These plants multiplied with ferns, fertilization took place directly in the inner tissue.
As a result of what direction of evolution arose wind-sour plants?Idioadaptation (from Greek. Ídios is its own, peculiar, special and adaptation), one of the main directions of evolution, in which private changes in the structure and functions of organs occur while maintaining the level of the organization of the ancestral forms. An example can serve IN
ethropylene plants - plants pollinated by wind, however, under different circumstances, they can also be pollinated by insects. Popile plants have very small and numerous flowers. Such plants produce a lot of pollen: one plant can produce millions of pollen grains. Many wind-sour plants (wood, aspen, alder, mulberry) flowers appear even before the dissolution of the leaves.
Winding plants. Plants whose flowers are pollinated by the wind and are called shielding. Usually their inexpressive flowers are collected in compact inflorescences, for example, in a complex spicy, or in a sweeper. They formed a huge number of small, light pollen. Shopping plants most often grow large groups. Among them there are herbs (Timofeevka, Mattik, Osoka), and shrubs, and trees (Ohshnik, Alder, Oak, Topol, Birza). And these trees and shrubs bloom simultaneously with the dissolution of the leaves (or even earlier).
In the wind-pinning plants, the stamens usually have a long stitching thread and carry a boot outside the flower. Pistol strokes are also long, "shaggy" - to catch flying dust in the air. These plants have some devices and to the fact that pollen does not be consumed in vain, and it is preferable to the stilts of the flowers of its own species. Many of them bloom on the clock: Some bloom early in the morning, the other day.
For plants pollinated by the wind, the following signs are characterized:
- Insparal small flowers, often collected in inflorescences, but small, minor;
- Curish storks and anthers on long hanging threads;
- Very small, light, dry pollen.
Examples of shielding plants: poplar, alder, oak, birch, hazel, rye, corn. Trees, pollinated by the wind, usually bloom in spring, to the dissolution of leaves, which would prevent pollen transfer.
The wind-sour plants own oaks and beech, alder and birch, poplar and plane fees, walnuts and lumps. In addition to trees, the wind is pollinated by many herbs living usually by large communities: cereals, sitters, crest, hemp, hops, nettle and plantain. On this list are only examples, it does not at all pretend to complete the list of shielding plants.
What kind of speciation is the adaptation to the nutrition of various foods of different types of bodies dwelling within a single range? Environmental in cases where the population of one species remains within its range (one territory), but they have different habitats. Under the influence of the driving forces of evolution, their gene composition varies. Through many generations, these changes can go so far that the individuals of different populations of one species will not be cross each other, biological isolation will occur, which is typical, as a rule, for different types.
Five types of cells were formed in connection with the food specialization: the big tit is powered by large insects in the gardens, parks; Lazorovka miners small insects in the creams of the bark in the kidneys; Crested tit is powered by seeds of coniferous trees; Gaiche and Moscow feeds mainly insects in the forests of different types.
What process plays a role in the formation of certain adaptations to the habitat among various organisms? Natural selection
Natural selection is the main driving factor in the evolution of organisms.
Natural selection is the result of hereditary variability and struggle for existence. Its main function is to eliminate individuals from the populations with unsuccessful, violating the process of adaptive formation by genetic combinations and the preservation of genotypes that do not interfere with the adaptive process. The effect of natural selection is determined by the fact that they survive and leave the offspring those organisms that are better adapted to changes in the environment.
1. Adaptations - features of the structure, vital activity, reproduction and development, allowing organisms, types and populations to survive in the habitat characteristic of them. Saving individuals with features useful for them in a certain habitat as a result of natural selection. Examples of fitness: the patronage of green grasshopper, river cancer, females openly nesting birds makes them imperceptible against the background of the environment; warning color of the bedlop soldiers and other "inconsiderable" animals that do not have special means of protection; The similarity of some types of flies on the shape of the body and painting with axes and bees, butterflies - with dry leaves, caterpillars - with knots of trees; Change coloring from other animals in different seasons of the year (Zayak-Skin). Adaptation of plants to cross-pollination, to the spread of fruit seeds, etc.
2. Relative character of fitness. The adaptability to the habitat is relative, useful only in those conditions in which it has historically formed. Mole has adaptations to life in the soil, but on the surface it is helpless; Jellyfish are adapted to life in water, but the eaves thrown ashore are dying, the poisons do not act on the eggs, they do not die in winter at low temperatures, but the sun rays are destructive for them; During molting, river cancer is helpless, even a mowing beetle can cope with him; Capuppet Belyanka Caterpillars Poisonous, birds do not eat them, but the riders are laying eggs in the caterpillars of this butterfly, the larvae of the rider, which are derived from eggs, feed on caterpillars of cabbage whitening.
3. Fitting of organisms to life in a certain habitat (on the example of aquatic animals). A large density of water compared to the ground-air sphere. In this regard, habitats in its highly specialized species, in which, in the process of evolution, adaptations were formed to reduce the energy costs for water resistance when moving. So, in the fish streamlined body shape, a fixed connection of its departments (head, torso, tail), the tiled location of the scales, the mucus covering the skin, the movement organs - fins. The formation of adaptations to movement in water is the main direction of the evolution of species inhabiting the aquatic environment (seals, cats, whales, etc.).
What selection contributes in new conditions to preserve individuals with changes to the genotype useful for them? Driving motive selection
The driving selection is the form of natural selection, when environmental conditions contribute to a certain direction of changing any characteristic or group of signs. At the same time, other possibilities for changing the sign are negative. As a result, in the population of generation to generation, the average values \u200b\u200bof the feature in a certain direction occurs. In this case, the pressure of the driving selection should respond to the adaptive capabilities of the population and the rate of mutational changes (otherwise the pressure of the medium can lead to extinction).
A modern case of driving selection is the "industrial melanism of English butterflies." That is, the butterflies inhabiting in industrial areas have a darker color (due to pollution) due to the industrial effects of the tree trunks, too, have darkened significantly, and light lichens died, because of which light butterflies have become better visible for birds, and dark - worse . In the 20th century, in a number of areas, the share of dark-painted butterflies reached 95%, while for the first time the dark butterfly (Morfa Carbonaria) was caught in 1848.
The driving selection is carried out when environmentally changed or adapting to new conditions when expanding the range. It retains hereditary changes in a certain direction, moving accordingly and the reaction rate. For example, when exploring the soil, as the habitat environment, various non-rigid groups of animal limbs turned into
As a result of which direction of evolution, pollination of plants insects arose? Idioadaptation (from Greek. Ídios is its own, peculiar, special and adaptation), one of the main directions of evolution, in which private changes in the structure and functions of organs occur while maintaining the level of the organization of the ancestral forms. An example can be the adaptations developed in insectopillary plants in the process of evolution:
1. Flowers are large single, bright.
2. Small inflorescences are usually collected in inflorescences, too bright.
3. Sweet juice nectar, located in a flower depth and produced by special glands - neckers.
4. The fragrance of flowers is enhanced in most cases by night. Such flowers are pollinated by night butterflies. Lily of the Lily, Rosa, Levka, Lilac - Make a gentle, thin fragrance, and clover flowers, apple trees, pears smelling with honey, therefore, they are always surrounded by ROOM bees.
5. Pollen is large, sticky, rough, easily sticks to the shaggy body of insects. Insect pollination is the most economical and effective way that is widely used in agriculture to increase the yield of plants. To this end, in the fields of buckwheat, with the gardens specially put the hives and get 2-3 times the harvest above.
1. What is the independent development of similar signs from different groups of organisms in similar environmental conditions? convergence 
2. Specify the driving force of evolution. Struggle for existence 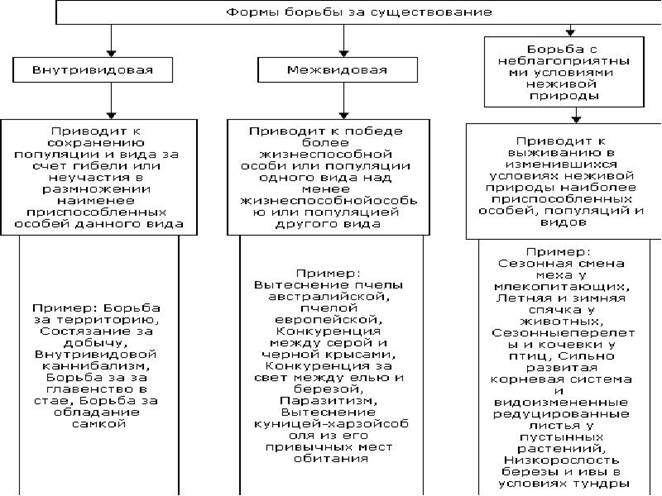
3. Mimicry - this is an example ... idioadaption
Mimicria (imitation, masking, Fr. Mimétisme, English. Mimicry) - the expression introduced into zoology initially (Bates) to designate some special cases of extreme external similarity between different types of animals belonging to various types and even families and detachments; It is usually, however, the same name denote all the pronounced cases of intelligent coloring and similarity of animals with inanimate objects.
In animals, one of the types of patronizing color and forms, in which the animal is similar to environmental objects, plants, in unbearable or predatory animals. Promotes the conservation of an animal in the struggle for existence. So, the sea needle fish looks like algae, among whom it hides. Mimicry in plants - similarities (shape, smell, color, etc.) with any other plants or animals. 

