Gameta in biology is ... the essence of the concept
Gameta is in biology Semi-body body, carrying a single chromosome set. Gamets play a key role in fertilization and intrauterine development. Consider the human body, in each somatic (not sex) the cell of which is 46 chromosomes, that is, the diploid set. Only in gates, the amount of chromosomes is 23. When these cells merge, the zygota with a complete set of chromosomes is formed.
This process will be considered in more detail below. Initially, we will analyze in detail what such a gamet in biology. This is a sex cell required for reproduction. But what is its structure and anatomy? Let's study this question more.
Gametogenesis
Gametogenesis - the process of ripening heamed in the body. Under it implies spermatogenesis (among individuals of male), and oogenesis (in female individuals). Gametogenesis is present in the life cycle of multicellular animals and plants: algae, mushrooms, arthropods, birds, amphibians, mollusks, mammals.
Anatomy Gamet
Women's goveta in biology is an egg cell. It is formed as a result of oogenesis. Eggs contain supply of nutrients necessary for the development of zygotes after fertilization. They are stationary and noticeable (about 100,000 times) are superior in size men's sexes.
Male goveta in biology is a spermatozoa. These cells are much less women's weights. They have flagella, which make spermatozoa movable and contribute to the promotion of female sex cells. In arthropods, spermatozoa do not have flavors, but it is rather an exception to the rules.
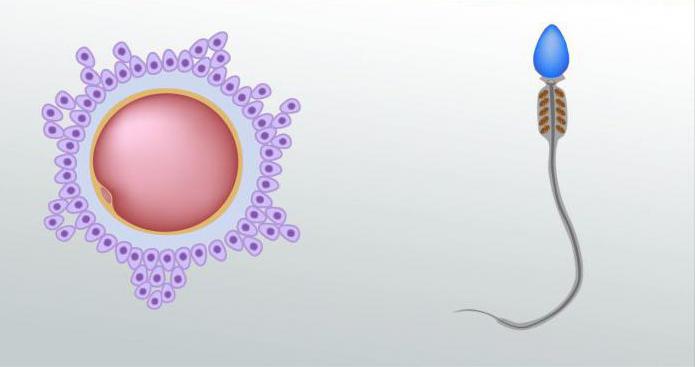
The picture below shows the images of male and female genital gamets - egg cells and spermatozoa.
Biological role
What is goveta in biology? Definition and functions are already described, we will deal with their biological role. Gamets play a key role in reproduction. Merging, male and female goveta form a zygota - a cell with a complete diploid set of chromosomes. In a human egg, there is only one type of chromosomes - x. Since men have both x and y-chromosome, then part of the spermatozoa is carried x, and part of the y-chromosome. Depending on what kind of spermatozoa varieties fertilizes the egg, the floor of the future child depends. Chromosome XX encoded the female floor, Hu is a male.
Immediately after fertilization, the zygota begins to develop and share. Eggs are a supply of nutrients in the form of a yolk. The zygote can be in an inactive state for some time, not to share and not develop before the onset of favorable conditions. This type of development is characteristic of some plants.
By the amount of nutrients, the eggs are divided into sharp (without yolk), oligolecital (with a small amount of nutrients), mesolocytal (with an average nutrient amount), polyletical (with a large number of yolk). It can be concluded that gamet in biology is a sex cell, without which the reproduction is impossible among the individuals of this species.
