Classification of animal world
The science of animal classification is called systematics or taxonomy. This science determines the related links between organisms. The degree of kinship is not always determined by external similarity. For example, the silent mice are very similar to ordinary mice, and Tupayi - on the protein. However, these animals relate to different detachments. But the battleships, the amusements and the sloths, completely dissimilar on each other, are combined into one squad. The fact is that related links between animals are determined by their origin. Exploring the structure of a skeleton and a dental system of animals, scientists determine which animals are closest to each other, and the paleontological finds of ancient extinct animal species help to establish more precisely related links between their descendants. Large role in the systematics of animals plays genetics- Science about the laws of heredity.
The first mammals appeared on Earth about 200 million years ago, separated from the visual reptiles. The historical path of the development of the animal world is called evolution. During the evolution, natural selection took place - only those animals were survived who managed to adapt to the environmental conditions. Mammals developed in different directions, forming many species. It happened that animals having a common ancestor at some stage began to live in different conditions and acquired different skills in the fight for survival. Their external appearance was converted, from generation to generation, useful changes useful for survival. Animals whose ancestors relatively recently looked the same, began to differ much from time to each other. Conversely, the species that had different ancestors and the last different evolutionary path are sometimes falling into the same conditions and, changing, becoming similar. So unforgettable views of the species acquire common features, and only science can be traced their history.
Classification of animal world
The living nature of the Earth is divided into five kingdoms: bacteria, simplest, mushrooms, plants and animals. The kingdoms, in turn, are divided into types. Exists 10 types Animals: sponges, msanka, flat worms, round worms, collar worms, intestinal, arthropods, mollusks, iglozzy and chord. Chordovy - the most progressive type of animals. They are combined by the presence of chord - the primary skeletal axis. The most highly mentioned chords are combined into vertebrate subtype. They have chord converted to the spine.
Kingdom
Types are divided into classes. Total exist 5 classes of vertebrate animals: Fish, amphibians, birds, reptiles (reptiles) and mammals (beasts). Mammals are the most highly organized animals from all vertebrates. All mammals unites what they feed their young milk.
Mammal class is divided into subclasses: Egglades and viviors. Egg-standing mammals multiply, laying eggs, like reptiles or birds, but young breeds milk. Viliable mammals are divided into infrackoms: sample and placental. The silent give birth to the underdeveloped young, which long time to run away in the brood mother's bag. Placentamentary germ develops in the womb and is born already formed. Placental mammals have a special organ - a placenta, which carries out the metabolism between the parent organism and the embryo in the period of intrauterine development. There are no silent and egg-placenta.
Types of animals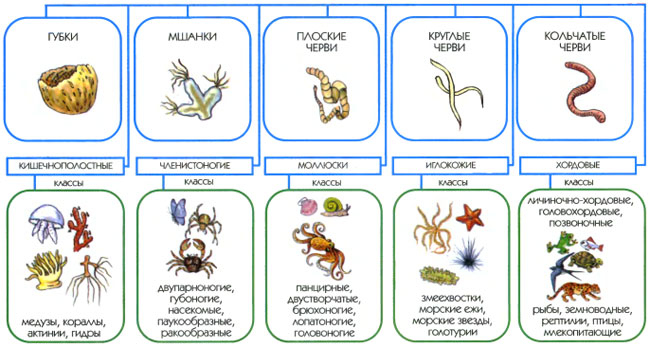
Classes are divided into squads. Total exist 20 mammals detachments. In the subclass of the eggs - one detachment: single-pass, in the infrared of the samples - one detachment: the sample, in the infrared of placental 18 detachments: incomplete, insectivores, helmet, manochable, primates, predatory, laston-energies, cetaceans, sirens, proboscatal, damas, pipes, Cavenogenic, lizards, rodents and towns.
Mammals class
Some scientists are isolated from the instrument of primates an independent squad of Tupayi, from the detachment of insectors, there are a squad of jumpers, and predatory and lastonovichi are combined into one detachment. Every detachment is divided into families, families - for childbirth, childbirth - on species. In total, about 4,000 mammals are currently living on Earth. Each animal is separately called a person.
