Roots of plants. Types of root system. Root functions. Root zones. Root modification.
Questions:
1. Functions root
2.Vides roots
3. Types of root system
4. Zones root
5. Validation of roots
6. Distributions of life in the root
1. Root functions
Root - It is an underground plant organ.
Basic root functions:
- reference: roots fix the plant in the soil and held throughout life;
- Nutrition: Through the roots, the plant receives water with dissolved mineral and organic substances;
- Possible: Nutrients can accumulate in some roots.
2. Types of roots
The main, apparent and side roots are distinguished. When germinating the seed, the germinal root appears, which turns into the main one. Pressure roots may appear on the stems. Side roots depart from the main and pressing roots. Pressure roots provide a plant with additional power and perform a mechanical function. Develop when extracting, for example, tomatoes and potatoes.
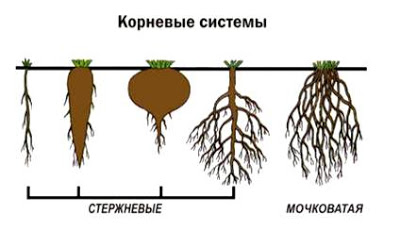
3. Types of root system
The roots of one plant is the root system. Root system is rod and urine. The main root is well developed in the rod root system. It has most dysfotic plants (beets, carrots). Perennial plants main root can die, and the food occurs due to the side roots, so the main root can only be traced in young plants.
The urine root system is formed only by the apparent and side roots. It has no main root. Such a system have monocotional plants, such as cereals, onions.
Root systems occupy a lot of space in the soil. For example, rye roots are distributed by 1-1.5 m and penetrate incur up to 2 m.
4. Root zones
In the young root, you can highlight the following zones: root case, division zone, growth zone, suction area.
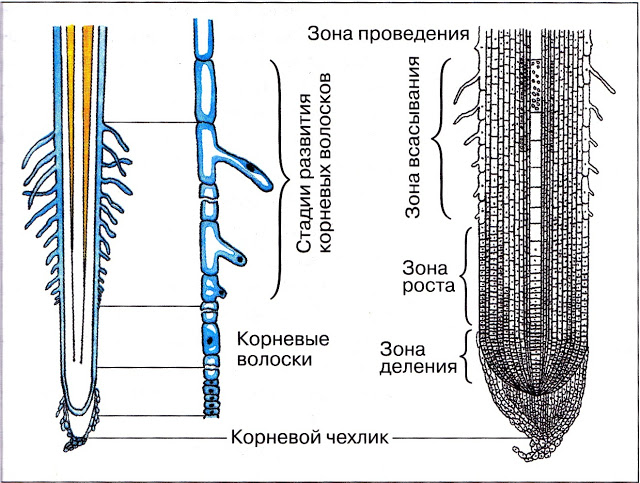
Root case It has a darker color, this is the most tip of the root. Root case cells protect the root tip from damage to solid soil particles. Celscellies are formed by coating cloth and are constantly updated.
Suction zone It has many root hairs, which pre-put elongated cells with a length of no more than 10 mm. This zone looks like a gun, because Root hairs are very small. Root hair cells as well as other cells have cytoplasm, core and vacuole with cellular juice. These cells are short-lived, die quickly, and their place forms new of the younger surface cells located closer to the root tip. The task of root hairs is suction of water with dissolved nutrients. The suction zone is constantly moving by updating cells. It is gentle and easily damaged during transplantation. There are cells of the main fabric.
Zone holding . It is above suction, does not have root-glossy, the surface is covered with a coating cloth, and in the thicker there is a conductive tissue. The cells of the area are vessels by which water with dissolved substances moves into the stem and leaves. There are also cells-vessels, according to which organic substances from the leaves come to the root.
The entire root is covered with mechanical tissue cells, which ensures the strength and elasticity of the root. Cells are elongated, covered with thick dish and filled with air.
5. Removing rootsThe penetration depth of roots into the soil depends on the conditions in which plants are located. The root length is influenced by the moisture, the composition of the soil, the eternal Merzlot.
Long roots are formed in plants in dry places. This is especially characteristic of the desert plants. So at the camel spines, the root system reaches 15-25 m in length. In wheat, the roots on the rapid fields are reached in length to 2.5 m, and on irrigated - 50 cm and the population increases.
Eternal Merzlota limits the growth of roots in the depth. For example, in the tundra in the dwarf birch roots only 20 cm. Surface roots, branched.
In the process of adaptation to the conditions of the roots of the plant roots, additional functions began to perform.
1. Root tubers perform the role of nutrient storage instead of fruits. There are such tubers as a result of thickening side or prescript roots. For example, dahlias.
2. Roots - modifications of the main root in plants such as carrots, turnip, beet. Roots are formed by the bottom of the stem and the top of the main root. Unlike fruits, they do not have seeds. Roots have two-year-old plants. In the first year of life, they do not bloom and accumulate in rooted many nutrients in root. On the second - they quickly bloom, using the accumulated nutrients and form fruits and seeds.
3. Root-trailers (suckers) - Cinema Corey, developing in plants of tropical places. They allow you to attach to vertical supports (to the wall, rock, tree trunk), making a foliage to the light. An example may be ivy and lomonos.
4. Bacterial tubers. The side roots of the clover, Lupine, Lucerne changed peculiarly. Bacteria settle in young side roots, which contributes to the absorption of gaseous nitrogen of soil air. Such roots acquire the appearance of the tuber. Thanks to these bacteria, these plants are capable of living on poor nitrogen soils and make them more fertile.
5. Air roots are formed in plants growing in wet equatorial and tropical forests. Such roots hang down and absorb rainwater from the air - they are found in orchids, bromelley, in some ferns, at Montster.
Air roots are appropriate roots formed on the branches of trees and reaching land. There are banyan, ficus.
6. Walker roots. In the plants growing in the tidal and tidal zone, wet roots develop. They hold high over the water at the husky orstive ground large fruitful shoots.
7. The breathing roots are formed in plants that have lacking oxygen for breathing. Plants grow in transduceously moist places - in the brandy swamps, plants, marine lines. Roots grow vertically up and overlook the surface, absorbing air. An example may be wolf, marsh cypress, mangrove forests.

6. Life processes in the root
1 - suction roots of water
The absorption of water with root hairs from the soil nutrient solution and carrying it through the cells of the primary bark occurs due to the difference in pressures and osmosis. Osmotic pressure in cells causes minerals to penetrate the cells, because Their content of salts in them is less than in the soil. The intensity of the absorption of water with root hairs is called sucking force. If the concentration of soil nutritional substances is higher than inside the cell, the water will come out of the cells and plasmolysis will come - the plants are covered. Such a phenomenon is observed in conditions of soil dryness, as well as with the unlimited making of mineral fertilizers. Root pressure can be confirmed using a series of experiments.
The plant with roots is lowered into a glass with water. On top of water to protect it from evaporation, the thin layer of vegetable oil and mention the level. In a day or two, the water in the tank dropped below the mark. Consequently, the roots of the water and submitted it up to the leaves.
Purpose: Find out the basic function of the root.
Sold in the plant the stalk, leaving the penetment with a height of 2-3 cm. On Penos, we put the rubber tube with a length of 3 cm, and on the upper end we put on the curved glass tube 20-25 cm. Water in the glass tube rises, and flows out. This proves that the water from the soil root sucks into the stem.
Purpose: Find out how the temperature affects the root.
One glass should be with warm water (+ 17-18ºС), and the other with cold (+ 1-2ºС). In the first case, the water stands out abundantly, in the second - there is little, or completely suspended. This is proof that the temperature strongly affects the root operation.
Warm water is actively absorbed by roots. Root pressure rises.
Cold water is poorly absorbed by roots. In this case, the root pressure drops.
2 - Mineral Food
The physiological role of minerals is very large. They are the basis for the synthesis of organic compounds and directly affect the metabolism; perform the function of catalysts of biochemical reactions; affect the cells of the cells and the permeability of the protoplasm; are centers of electrical and radioactive phenomena in plant organisms. With the help of the root, mineral nutrition of the plant is carried out.
3 - Breathing of roots
For normal growth and development of the plant, fresh air is required to the root.
Purpose: Check the availability of breathing in the roots.
Take two identical vessels with water. In each vessel, we will place developing seedlings. Water in one of the vessels every day is saturated with air with a pulverizer. On the surface of the water in the second vessel, the thin layer of vegetable oil, as it delays air flow into the water. After some time, the plant in the second vessel will cease to grow, will inhabit, and in the end will die. The death of the plant comes due to a lack of air necessary for the respiration of the root.
It has been established that the normal development of plants is possible only if there are three substances in the nutrient solution - nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur and four metals - potassium, magnesium, calcium and iron. Each of these elements has an individual value and cannot be replaced by another. These are macroelements, their concentration in the plant is 10-2-10%. For the normal development of plants, microelements are needed, the concentration of which in the cell is 10-5-10-3%. This is a boron, cobalt, copper, zinc, manganese, molybdenum dr. All these elements are in the soil, but sometimes insufficient. Therefore, mineral and organic fertilizers contribute to the soil.
The plant is normally growing and developing in the event that in the surrounding root medium will contain all the necessary nutrients. Such a medium for most plants is soil.
