Plant organs: root.
Root - This is an axial vegetative organ plant with unlimited top growth, positive geotropism, having a radial structure and non-carrier.
Roots hold a plant in the soil. Through the roots, the plant gets water and minerals from soil.
The roots of the plant form the root system.
Main Developed from the root of the embryo. Podep horses grow from the stem, side roots - from the main and apparent.
Rod root system
well developed main root
Characteristic for dicotyledonous plants (dandelion, carrots)
Urine Root system
the main root does not stand out among the apparent
Characteristic for monocotional plants
Thanks korni. The plant is fixed in the soil and receives water and minerals from it. Sometimes the root performs additional functions - is a vegetative organ organ, performs the synthesis of organic substances or spares nutrients. In order for the plant to be firmly held in the soil and in sufficient quantities received water and mineral salts from it, it should have a developed root system. For example, the root cabbage the root system reaches a depth of 1.5 m. And at the camel spines - up to 20 m., And the diameter of the root system of trees is 2-5 times the diameter of the crown.
The main functions of the root are suction and reference. The root growth is carried out due to the division of the cells of the top educational tissue (meristems). Small and gentle, intensively divided cells of the meryshes are covered outside the root case. It is characterized by physiological regeneration - permanent death of old cells and new education. Above is the growth zone, then the suction zone with root hairs and even higher - the area of \u200b\u200bthe conduct. The absorption of water and mineral salts by the root occurs passively (according to the laws of diffusion and osmosis) and actively (with energy costs).
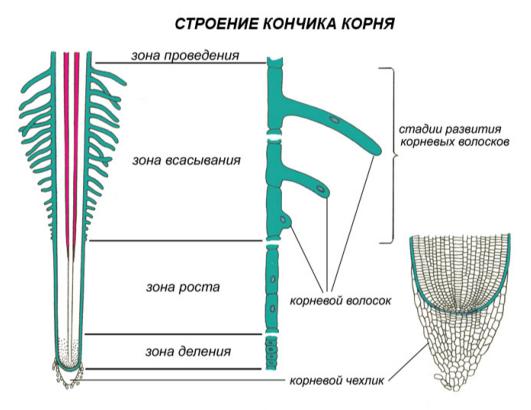
Water incoming through the suction zone with dissolved mineral salts is supplied to the above-ground organs of the plant along the root vessels lying in the zone of nutrients. The absorption of water and mineral salts by the root occurs passively (according to the laws of diffusion and osmosis) and actively (with energy costs). Water in the soil has a lower concentration of organic substances compared to the contents of root hairs. Therefore, due to the difference in osmotic pressure, water moves from the soil into the outer cells of the root.
For normal growth and development of the plant, it is necessary to come to its roots. Fresh air arrived. With the breath of the root cells absorb oxygen and isolated carbon dioxide. In some plants, nutrients are reserved in rootfields - modified roots. Root tubers from Georgin, Root-clothespins in Ivy, air roots in orchids are all examples of radiation modification.
