Arrangement of leaves on the stem
There are three main types of leaf arrangement: spiral or alternate - one leaf leaves each node of the stem (oak, birch, cereals, etc.), opposite - two leaves sit on each node (lilac, mint), whorled - leaves each node three or more leaves (oleander). There is also a basal rosette of leaves - this is a shoot with shortened internodes and close nodes (plantain, dandelion) (Fig. 43).
Rice. 43. Leaf arrangement: 1 - alternate, 2 - opposite, 3 - whorled, 4 - basal rosette of leaves.
Chapter 4
Generative organs are organs that perform the function of sexual reproduction. In angiosperms, it is a flower, an inflorescence and derivatives of a flower, a seed and a fruit.
flower morphology
A flower is a modified shortened shoot adapted for the formation of gametes, pollination, fertilization and the formation of fruits and seeds.
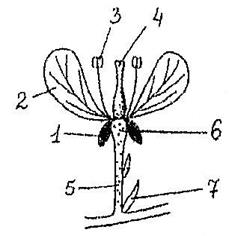
Rice. 44. Parts of a flower.
1. Calyx - a collection of sepals, protects the flower in bud.
2. Corolla - a set of petals, protects the stamens and pistils, attracts insects.
3. Androecium - a collection of stamens.
4. Gynoecium - a collection of carpels.
5. Pedicel - attaches the flower to the stem.
6. Receptacle - an expanded part of the stem, where all parts of the flower are attached.
7. Bract - leaf at the base of the pedicel.
According to the features of symmetry, flowers can be divided into actinomorphic, or regular, and zygomorphic, or irregular. Through the corolla of a regular flower, 2 or more planes of symmetry can be drawn (apple flower) (Fig. 45, 3-4, 9-11). Only one plane of symmetry can be drawn through a zygomorphic flower (Fig. 45, 1-2, 5-7).
Perianth - consists of a calyx and a corolla. It is simple and double. A simple perianth consists of equally colored parts. The simple calyx perianth is colored green (crow's eye), and the corolla consists of brightly colored parts (tulip).
The calyx is composed of green sepals. Sepals are free, in this case the calyx is called separate-leaved or free-leaved. Sometimes the sepals grow together. This is a spiky calyx. In plants of the rose family (strawberries), a second circle of sepals is formed outside the calyx, these are subcalyxes.
Corolla - consists of colored petals. Distinguish separately and jointly petaled corollas. In interpetal corollas, the lower fused part is distinguished - the tube, and the upper expanded part - the limb.
Asymmetric corollas come in different forms:
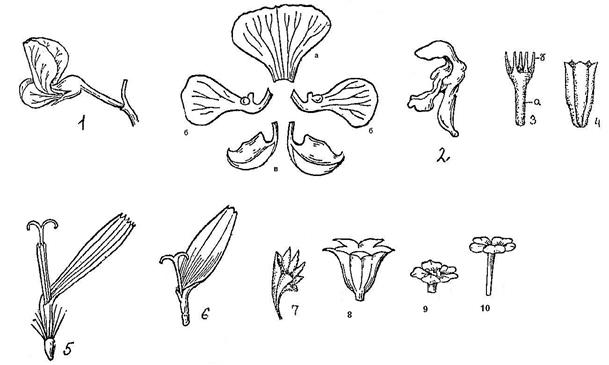
Rice. 45. Types of cleavage corollas: 1 - moth (a - sail, b - oars, c - boat); 2 - two-lipped; 3 - tubular: a - corolla tube, b - limb; 4 - tubular; 5 - reed; 6 - false tongue; 7 - funnel-shaped; 8 - bell-shaped; 9 - wheel-shaped; 10 - tubular-wheel-shaped.
The moth corolla consists of a sail, two oars and a boat fused from two petals. Two-lipped - the upper lip grows together from two petals, and the lower one from three. Tubular has a long tube (a) and a bend (b). At the reed corolla, five petals grow together into one plate. False-lingual - three petals grow together into one plate. Funnel-shaped - has a long tube and a wide limb.
Androecium
Androecium - a collection of stamens of one flower. In some flowers, there are no stamens - these are unisexual female flowers, and in unisexual male flowers, on the contrary, there are only stamens. Each stamen consists of a filament (1) and an anther (2). The anther has two halves connected by a binder. Pollen grains form in the anther nests (Fig. 46).
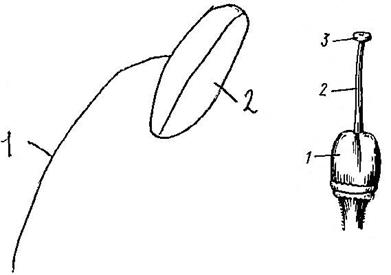
Rice. 46. Fig. 47.
Gynoecium - a set of carpels of one flower, forming one or more pistils. The pistil consists of a stigma (1), style (2), ovary (3), one or more ovules (Fig. 47). The ovary of the pistil protects the ovules from drying out, being eaten by insects, and temperature fluctuations. A pistil formed from one carpel is called simple, and from two or more fused carpels it is called complex. A gynoecium consisting of one simple pistil is called monocarpous. The apocarpous gynoecium consists of two or more free simple pistils. In the process of evolution, the carpels fused in different ways, forming a cenocarpous gynoecium (Fig. 48).
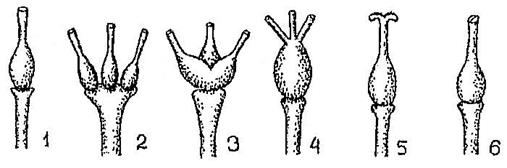
Rice. 48. Types of gynoecium. 1 - Monocarp (from one carpel), 2 - apocarp (from several free, not fused carpels), 3-6 - cenocarp (with varying degrees of fusion of carpels).
Depending on the position of the ovary of the pistil in relation to other parts of the flower, the upper, middle and lower ovaries are distinguished (Fig. 49). With the upper ovary, other parts of the flower are located under it, and the ovary itself is completely free. With an average ovary, parts of the flower fuse with it to about half the ovary. With a lower ovary, parts of the flower are located above the ovary, and their lower parts grow together with its outer wall.
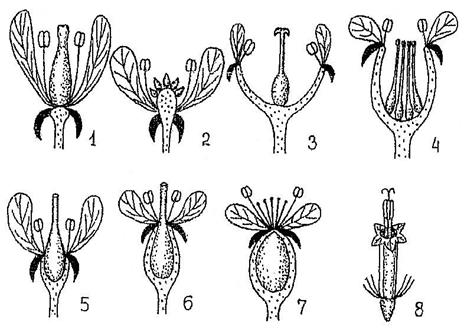
Rice. 49. Types of ovary. 1-4 - top, 5 - middle, 6-8 - bottom.
