The structure of the leaf of the plant. Features of the structure of the sheet
The sheet is a very important organ of the plant. This is part of the escape, the main functions of which are transpiration and photosynthesis. The features of the structure of the sheet consist in its high morphological plasticity, large adaptive capabilities and diversity of forms. The base can be expanded in the form of welders - leaf-shaped oblique formations on each side. In some cases, they are so big that they play a certain role in photosynthesis. Highlights are raising to the cut or free, they can be shifted on the inner side, and then called the stuffed.
The external structure of the sheet
Leaf plates are not the same in size: they can be from a few millimeters to ten and fifteen meters, and by palm trees - even twenty meters. The structure of the sheet determines the life expectancy of the vegetative organ, it is usually short - no more than a few months, although some are from one and a half to fifteen years. Form and size are inherited features.
Parts of leaves
The sheet is a side vegetative organ that grows from the stem, at the base of the growth zone and bilateral symmetry. Usually it consists of a stuff (with the exception of seating leaves) and a sheet plate. In a number of families, the structure of the sheet also assumes the availability of hostesses. The external organs of plants may be simple - with one plate, and complex - with several plates. 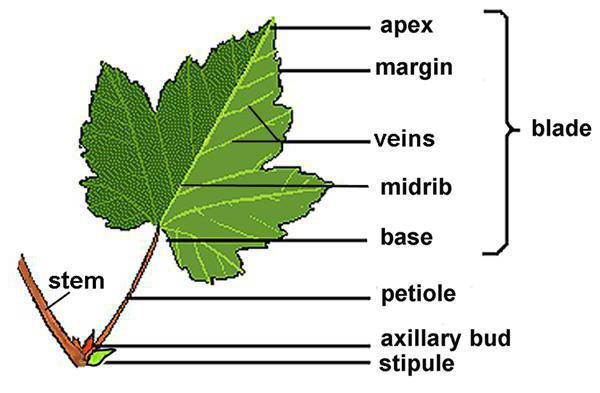
Sheet pillow (base) is the part that connects the sheet with the stem. Here, the educational tissue gives an increase in a stiff and a sheet plate.
Puffs - a narrowed part, with its base connecting the stem and sheal plate. It focuses the sheet relative to the light, stands as a place where the insertation of the educational fabric is located, due to which the vegetative organ increases. In addition, the petiole weakens the strikes on the leaf during the rain, wind, hail.
Sheet plate is usually a flat extended part that performs the functions of gas exchange, photosynthesis, transpiration, and some species also have a function of vegetative reproduction.
Speaking about the anatomical structure of the sheet, it is necessary to say about Hightails. These are sheets of paired formation at the base of the vegetative organ. When deploying the sheet, they may be discharged or saved. Designed to protect the stuffed side kidneys and inserting educational fabric.
Complex and simple leaves
 The structure of the sheet is considered simple if it has one sheet plate, and complicated - if several or many plates with joints. Due to the last plates of complex leaves, it is not falling together, but one. But some plants may have fallen and entirely.
The structure of the sheet is considered simple if it has one sheet plate, and complicated - if several or many plates with joints. Due to the last plates of complex leaves, it is not falling together, but one. But some plants may have fallen and entirely.
One-piece leaves in shape can be blade, separate or dissected. In the blade sheet, cutouts on the edge of the plate are up to 1/4 of its width. For a separate organ, a greater deepening is characterized, its blades are called shares. The dissected sheet along the edges of the plate has cuts that reach almost to the medium vein.
If the plate is elongated, with triangular segments and shares, the sheet is called a podgoid (for example, at a dandelion). If the lateral shares are reduced to the base, are non-equinable, and the final share of the rounded and large, it turns out a lead-shaped outer organ of the plant (for example, radish).
The structure of the sheet with several plates is significantly different. Painty-bounded, three-grained, peristoid bodies. If the complex sheet includes three plates, it is called a triple, or three-closed (for example, male). Palcounted sheet is considered when its sweets are attached to the main stiff at one point, and the plates are diverted radially (for example, lupine). If the side plates on the main cutter are available on both sides along the length, the sheet is called the peristoids. 
Forms of whole plates
In different plants, the shape of the sheet plates are unequal in the degree of dismemberment, the outline, the formation of the base and the tops. They may have round, oval, triangular, elliptic and other outlines. The plate is elongated, and its free end can be blunt, pointed, sharp or pointed. The base is drawn and narrowed to the stalk, sometimes heart-shaped or rounded.
Attaching a stalk
Considering the structure of the leaf of the plant, you should say a few words about how it is attached to run. Attachment is carried out using long or short cuffs. There are also seated leaves. Some plants of their foundations are growing with escape (sliding sheet), and it happens that the escape is permeated with a plate (pierced by a sheet).
Internal structure. Skin
Epiderma (Top Skin) is a coating fabric located on the facing side of the plant organ, often covered with cuticle, hairs, wax. The internal structure of the sheet is such that it has a skin that protects it from drying out, mechanical damage, penetration of pathogenic microorganisms to the inner tissues and other adverse effects.
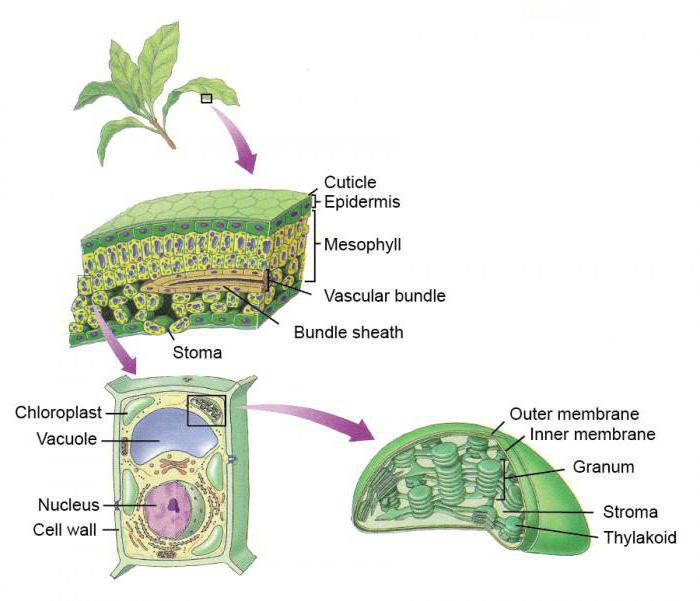
Skin cells are alive, they are different in shape and sizes: Some - transparent, large, colorless, tightly adjacent to each other; Others are smaller, with chloroplasts that give them a green color, such cells can change the shape and are placed in pairs.
Stoma
Skin cells can be given apart from each other, in which case the gap appears between them, which is called the Ustichnaya. When the cells are saturated with water, the dust opens, and with a fluid outflow, it closes.
The anatomical structure of the sheet is such that the air flows into the internal cells through the nutritional slots and the gaseous substances are out of them through them. When the plants are not sufficiently provided with water (it happens in hot and dry weather), the dust closes. So representatives of the flora defend themselves from the drainage, since with closed allocated slots, water vapors do not exit and persist in interclausers. Thus, in the arid period of the plant retain water.

Basic fabric
The internal structure of the sheet does not cost without a columnar tissue, the cells of which are located in the upper facep to the light, are tightly adjacent to each other, have a cylindrical shape. All cells have a thin shell, core, chloroplasts, cytoplasm, vacuol.
Another major fabric is spongy. Her cells in the form round, are located loose, there are large interclauses, filled with air between them.
What will be the structure of the plant leaf, which amount of the spongy and the columnal tissue is formed, depends on the lighting. In the leaf grew up on the light, the columnar cloth is much more developed than those that they grow under dimming conditions.
